for Drone Systems

Introduction
Welcome to the official blog of BeRAM Drones I'm Yogiraj Chauhan, a 3rd year Electronics and Computer Science student at RCOEM, Nagpur. At BeRAM, we believe in innovative, resourceful, and cost-effective solutions that address real-world challenges. During my internship, I have worked on Drone assembly, sensor testing, system setup and component debugging to align with project goals.
What is Sensor Integration?
Sensor integration is the process of incorporating physical sensors into an electronic system, such as an IoT device or embedded system. Its primary purpose is to gather real-world data like temperature, motion, or light, and make it usable for analysis, automation, or control tasks. It's an end-to-end process that involves embedding sensors into digital systems, ensuring their outputs are accurate, timely, and secure for various application layers. This spans hardware interfacing, protocol adaptation, middleware development, real-time communication, and analytics.
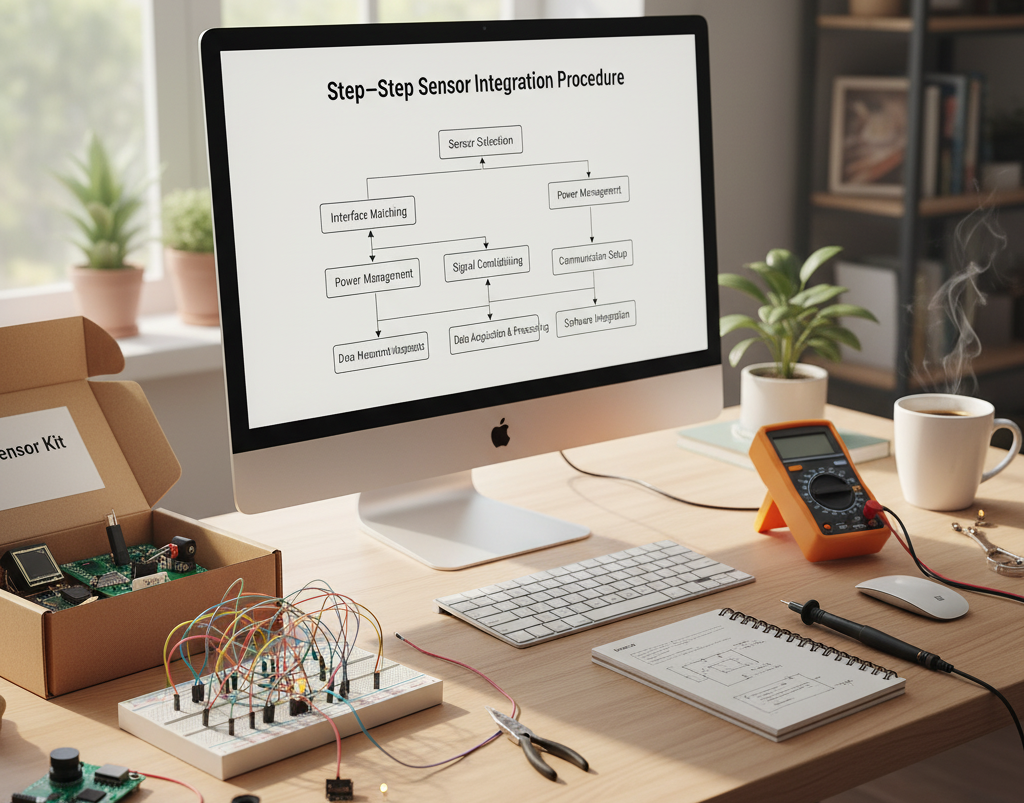
Drone-Specific Sensor Integration Procedure
- Sensor Selection
- Interface Matching
- Power Management
- Signal Conditioning
- Communication Setup
- Data Acquisition & Processing
- Software Integration
Challenges in Sensor Integration
Sensor integration presents several challenges that must be addressed for successful deployment. These include ensuring compatibility, managing data flow, maintaining power efficiency, and securing data transmission.
- Interoperability
- Data Synchronization
- Latency
- Power Efficiency
- Security
Best Practices for Sensor Integration
Adhering to best practices ensures robust, reliable, and secure sensor integration. These practices cover design, calibration, software abstraction, and security measures.
- Modular Design: Use modular design for easy sensor swapping and maintenance.
- Regular Calibration: Calibrate sensors regularly to maintain accuracy and reliability.
- Middleware/Drivers: Utilize middleware or drivers to abstract hardware details, simplifying development.
- Secure Data: Secure data transmission with TLS/SSL for protection against threats.
- Fault-Tolerance: Design for fault-tolerance and redundancy to ensure continuous operation.
Real-World Use Cases
- Smart Cities: Traffic and pollution sensors for urban planning and environmental monitoring.
- Healthcare: Biosensors for vital sign monitoring and integration into wearables (ECG, SpO2).
- Smart Agriculture: Soil moisture and ambient sensors for automated irrigation, multispectral sensors on drones.
Conclusion
Sensor integration stands at the heart of today’s technological revolution, enabling devices to bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds. From smart cities and healthcare to agriculture and industrial automation, seamlessly integrated sensors empower systems to collect accurate real-time data, make intelligent decisions, and drive meaningful action.
At BeRAM Drones, our mission goes beyond implementing sensors—we focus on creating resourceful, cost-effective, and scalable solutions that transform raw data into actionable insights. As industries embrace IoT and automation, mastering sensor integration is not just an advantage—it is a necessity for building smarter, more connected, and future-ready systems.